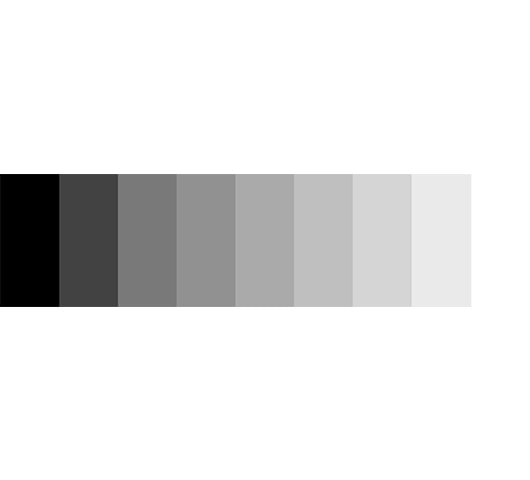Our online eye test:
Test yourself!
How well do you see?
Our online eye test: Test yourself!
Visual impairments often develop over time and unnoticeably. Our vision test gives you an initial impression of your eyes’ ability to see. Test your vision now! Please note: A self-test does not replace the professional eye test with an optometrist or ophthalmologist.
Defective vision
If you notice that you cannot see well close-up or from a distance, then you probably suffer from defective vision.
If you are short-sighted, you can see well close-up without spectacles, but in the distance everything is blurred and unclear. The most frequent cause is a longer eyeball (length myopia) meaning that the image emerges before the retina and therefore cannot be seen sharply.
Long-sightedness occurs in most cases from a shorter eyeball (length hyperopia). The image emerges behind the retina and is not shown sharply. For distance vision this can still be balanced relatively well for some time, but close-up vision is not clear.

Presbyopia
When your arms are too short to read: Presbyopia is the most frequent cause of defective vision as we get older.
Our eyesight in the near area deteriorates as we get older and books or letters have to be read with an extended arm. The ageing process of the eye and the accompanying decreasing elasticity of the eye lens are responsible.
In order to balance our presbyopia, a progressive lens is suitable for infinitely variable sharp vision in all distances. At the workplace you benefit from special computer spectacles with Ergo® near comfort lenses.

Corneal curvature
Curved means that the cornea is not evenly shaped. Mild astigmatism is quite common.
Approx. 70% of all spectacle wearers are astigmatic. This means they have a corneal curvature. The different deformations of the cornea mean that the light is refracted differently and as a result, for example, round objects appear oval due to the distortion. This also explains the synonym “astigmatism”.
Corneal curvatures are corrected with toric lenses. They can be optimally balanced out with Rodenstock lenses – and you can fully utilise your vision potential again.
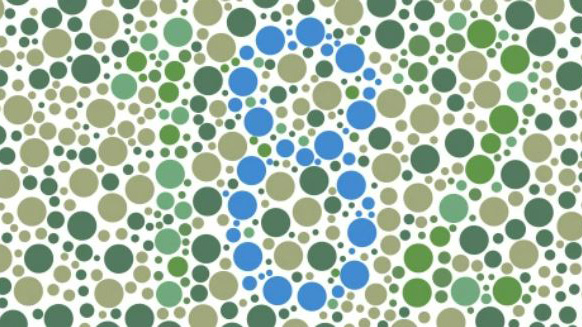
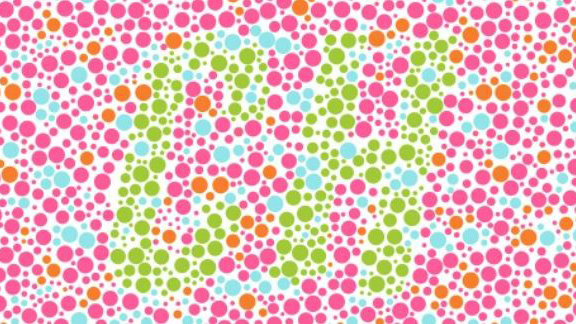
Color perception
A colour vision deficiency is also innate in most cases with many visual impairments. Men are more commonly affected than women.
Colour vision deficiency or colour blindness? The two terms are often used as synonyms. But the hereditary vision problems are by no means equal: Protanomaly or deuteranomaly describes a red or green colour vision deficiency. This means the colours can only be detected when they are particularly saturated and strong.
Colour blindness for different colours is called anopsia. In the case of protanopia or deuteranopia the affected individual is missing the colour receptors for red or green on the retina and the two colours are perceived as bright grey shades. Unfortunately, there are no treatment options available for a colour vision deficiency or colour blindness. However, with tinted lenses the frequently occurring light sensitivity can be alleviated.

Retina function
The retina is a projection area on which our environment is depicted. It guides the impulses caused by bursts of light to the brain.
The Amsler vision test is used to examine the retina. With the Amsler grid diseases affecting the centre of the retina can be identified. In the case of macular degeneration, the central visual acuity of an eye is fully or partially lost. As only the centre of the retina is affected, the field of vision at the sides is retained.
Macular degeneration must be treated professionally. If you do not have a good feeling with this vision test, please visit your ophthalmologist.
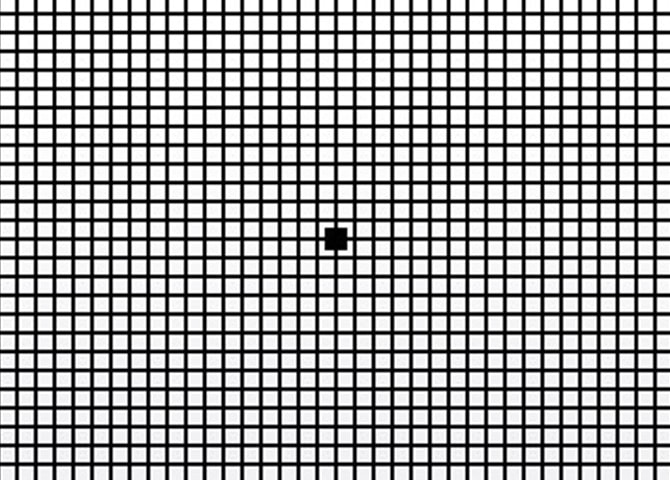
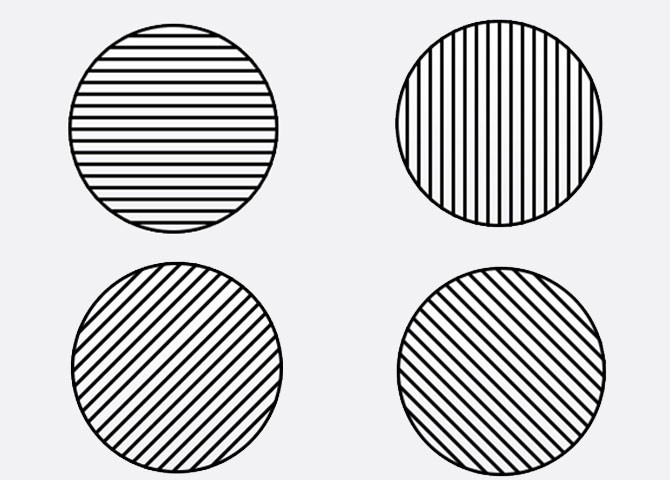
Field of Vision
The field of vision, also called field of view, is what we see when we look directly ahead with our head straight.
It covers everything that is depicted on the retina. Here it does not matter whether the things are sharp – also the environment that one perceives but cannot detect clearly is also included.
Improve your vision at a monitor
A few simple measures and a special pair of computer or near comfort spectacles guarantee improved visual comfort when working at the monitor. The settings of your monitor also play a role here.